GSTR-3 is a monthly GST return to be filed by 20th of every month, by all regular taxpayers registered under GST in India. GSTR-3 is an accumulation of outward and inward supplies during the previous month, which will be auto-populated via GSTR-1 and GSTR-2.
GSTR-1: Captures details of outward supplies, i.e. sales.
GSTR-2: Captures details of inward supplies, i.e. purchases.
GSTR-3: Captures both [inward + outward] supplies.
The article aims to apprise you in depth about the applicability and scope of GSTR-3, GSTR 3 format, GSTR form.
- What does GSTR-3 contain?
- What if GSTR-3 is not filed / filed late?
- Can GSTR-3 be revised?
- Due date for GSTR-3.
1. What does GSTR-3 contain?
Mostly, the headings under GSTR-3 are auto-populated fetching data from GSTR-1 and GSTR-2 and hence will involve minimal time to fill in. There are 15 headings which form the framework of GSTR-3, detailed as under:
2. Name of the Taxpayer:
- Both the individual and the trade name will populate.
- Month and Year: The correct month and year for which the GSTR-3 is being filed, has to be filled in.
There are 2 parts of GSTR-3. Part A auto-populates from GSTR-1, GSTR-1A and GSTR-2. Part B needs to be filled manually.
Part A [Auto-populates up till point 11 and also point 15]
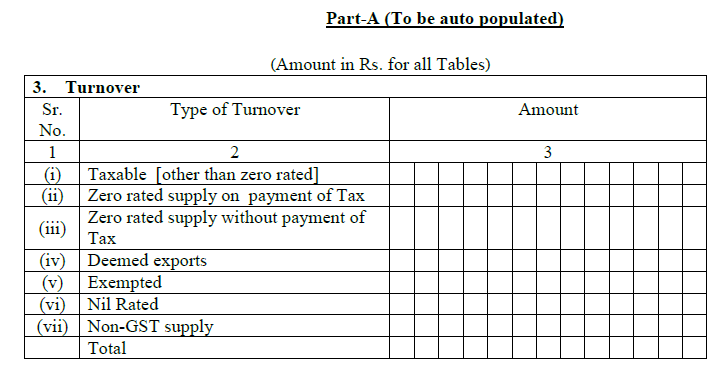
3. Turnover:
This comprises of the overall turnover of all the supplies, segregated in:
- Taxable turnover except zero rated: Comprises of normal sales to both registered and unregistered buyers
- Zero rated supply on payment of tax: Comprises of exports which are paid through IGST and later retrieved as refund
- Zero rated supply without payment of tax: Comprises of exports which are paid through bond/LUT
- Deemed exports: Comprises of items sold to SEZ, when the goods actually do not leave India
- Exempted: Comprises of supplies, exempt from GST
- Nil rated: Comprises of supplies which attract 0% GST
- Non GST supply: Comprises of supplies, which does not fall under GST like petrol, electricity etc.
4. Outward Supplies:
It is an auto populating field, which fetches data from GSTR-1 and comprises of a snapshot of the entire sales during a month.
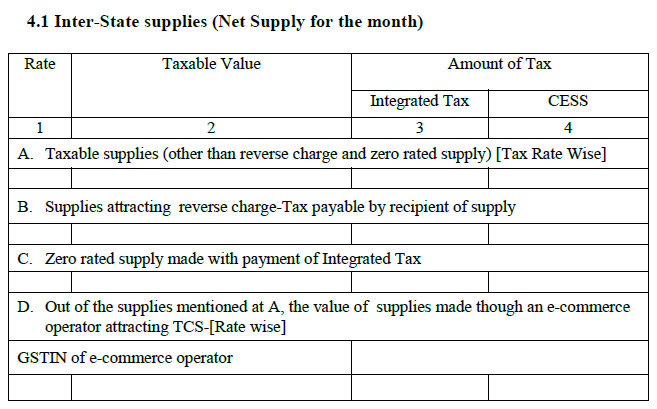
4.1 Inter-state supplies [net supplies for the month]: The total inter-state sales is captured here under the following heads:
A. Taxable supplies except reverse charge and zero rated supply:
Captures the total sales except on which reverse charge applies and exports
B. Supplies attracting reverse charge-tax payable by recipient of supply:
It comprises of sales, where the buyer will be paying GST under reverse charge.
C. Zero rated supply paid with IGST:
Comprises of exports paid through IGST and reclaimed as refund.
D. Supplies made through an e-commerce operator liable for TCS, out of the supplies mentioned in A:
The point A mentions the total sales, which includes e-commerce sales too. This heading will just fetch the e-commerce sales specifically, displaying the GSTIN of the e-commerce operator.
** The zero rated supplies, which are made without paying the GST will not get included, like exports through bond / LUT.
** Amendments of supplies originally made under reverse charge basis will not be included in table 4.
4.2 Intra-state supplies [net supplies for the month]:
This is a replica of the above heading and the only difference is that it will capture the details of the intra-state sales.
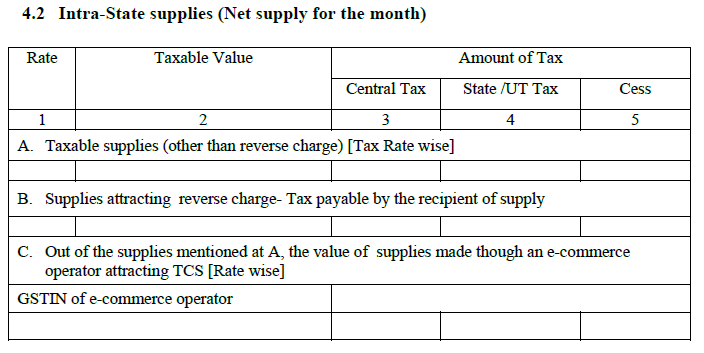
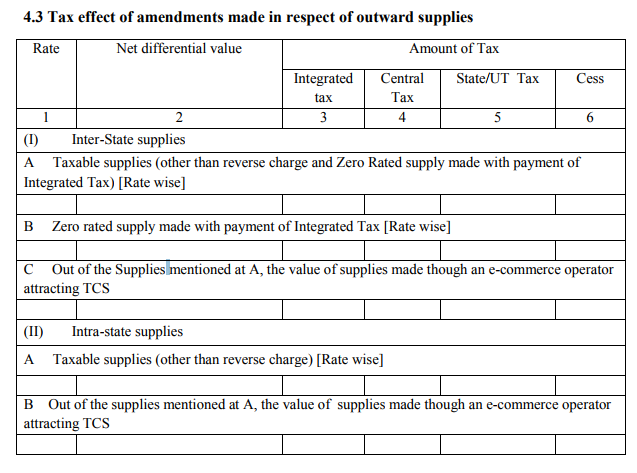
4.3 Tax effect of amendments in terms of outward supplies:
Any changes made to the sales invoice will get captured here. Changing the invoice amount has a direct impact on ITC, which in continuation impacts the revenue of the government. This heading basically aims to capture any such change and its ripple effects.
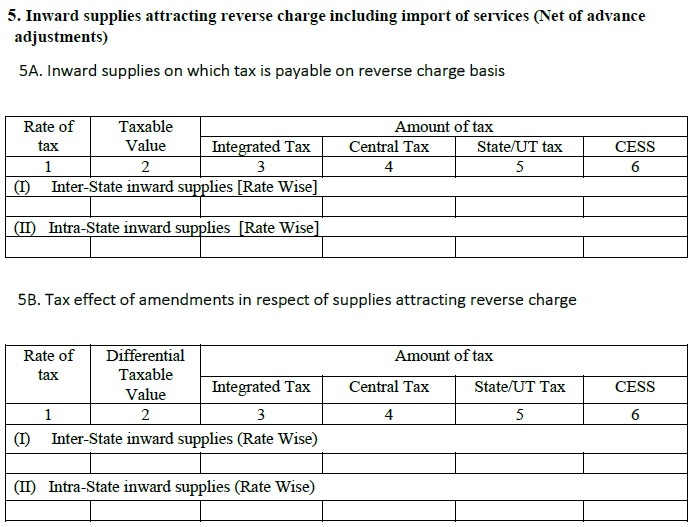
5. Inward supplies with reverse charge including import of services [Net of advance adjustments]:
This heading will auto-populate and fetch data from GSTR-2 comprising of all the [purchases made + supplies received] during the month.
5A. Inward Supplies with tax payable on reverse charge:
- It comprises of transactions where the reverse charge is applicable, i.e. the buyer pays it.
- Includes sales both from inter-state and intra-state and the tax liability arising due to reverse charge is the sum of net of invoices, debit/credit notes, advances paid and adjustment of advances.
5B. Tax effect of changes in terms of supplies with reverse charge:
It will capture the purchase amendments [excess / under payment] attracting reverse charge. This heading is basically meant to keep a track of the changed purchase invoices and also capture the change in the tax amount therefore.
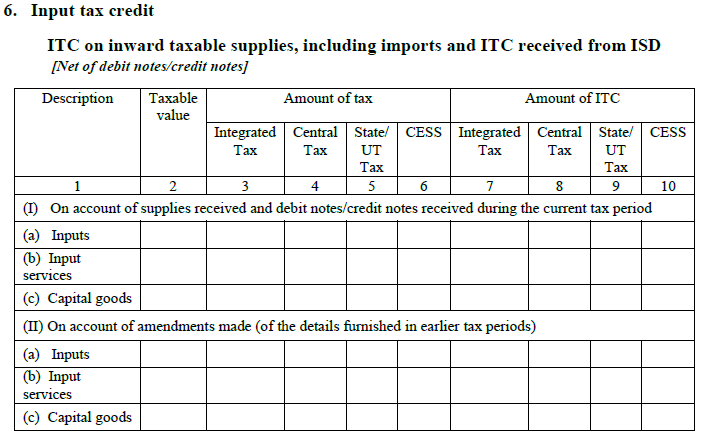
6. Input Tax Credit:
This heading captures the ITC on inward taxable supplies including imports and ITC received from ISD [Sum of debit and credit notes]
Part I: It will individually show the summarized ITC for a calendar month under:
- Input products: The raw material
- Input Services: Any consulting fees
- Capital goods: A printer etc.
This heading will also reflect the ITC received from a Input Service Distributor after the adjustment of the debit/credit notes.
Part II: It will show the changes made to earlier month’s details [if any] and their subsequent impact on ITC.
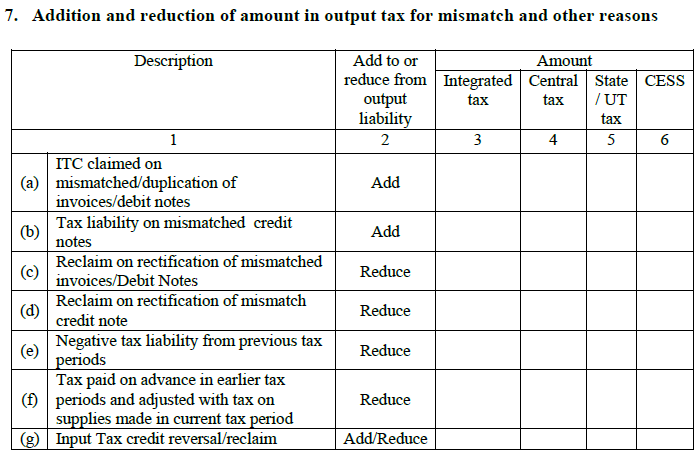
7. Addition/reduction in output tax for mismatch and other miscellaneous reasons:
This will fetch data from GSTR-2 about any sort of amendments in output tax [+/-] and the subsequent tax liability between the original return and also the current month’s changes.
A. ITC claimed on mismatched/duplication of invoices/debit notes:
The mismatch of invoices may result in the double claiming of ITC. The ITC claimed in excess due to doubling of invoices will be reversed and added to the overall tax liability.
B. ITC claimed on mismatched/duplication of credit notes:
ITC will also be impacted by the incorrect or duplication of credit notes. Excess ITC claimed due to this will be reversed and added to the overall tax liability.
C. Reclaim on correction of mismatched invoices/ debit notes:
When the mismatch leads to claiming of lower ITC, the balance amount gets deducted from the overall tax liability. This heading is just the opposite of point ‘a’.
D. Reclaim on correction of mismatched credit notes:
This is opposite to point ‘b’ and will be treated in the same way as ‘c’E
E. Negative tax liability carry forwarded from the previous tax periods:
This happens when the tax is paid in excess previously and so will get reduced from the overall tax liability.
F. Advance taxes paid previously and adjusted with the tax on supplies in the current month:
This heading mentions the amount of advance tax paid in the previous months for the supplies made in the current month.
G. Input Tax Credit reversal:
This heading captures the ITC being refunded for any other reason.
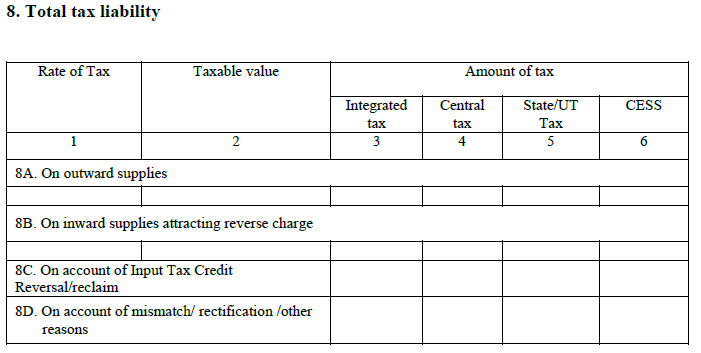
8. Total tax liability:
This is the deciding section, which tells you, how much total tax has to be paid and under which tax head – CGST/SGST/IGST segregated into the following headings:
8A. Outward Supplies:
The tax on normal sales including the inter-state sales is mentioned here.
8B. Inward Supplies under Reverse Charge:
Tax on purchases under reverse charge is mentioned here.
8C. ITC Reversal:
This field fetches data from the table 11 of the GSTR-2 and provides the additional tax payable or any reduction available incurring due to the ITC reversal.
8D. For reasons of mismatch:
Tax liability arising due to the mismatch, rectification or any reasons come here.
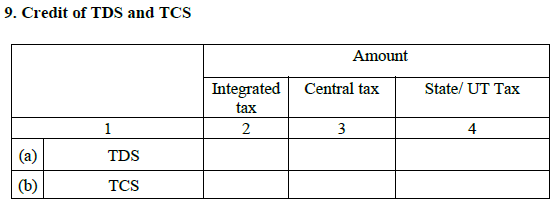
9. TDS and TCS credit:
TDS and TCS will be deducted from the overall tax liability to ascertain the tax amount to be paid.
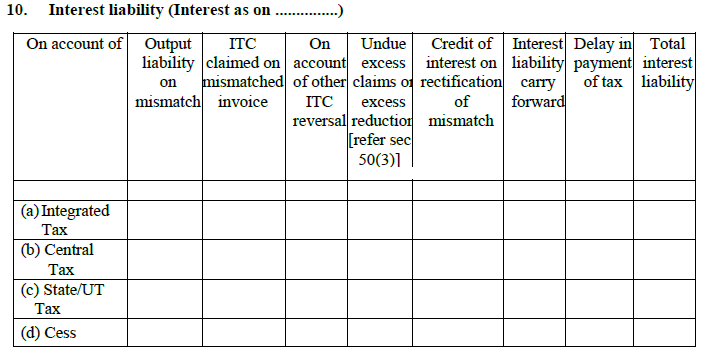
10. Interest liability:
Interest @18% per annum is applicable on any delay of tax payment and is calculated on the outstanding amount of tax only. Next day of filing [20th of every month] to the date of payment is to be considered as the time period for calculating the interest.
The heading captures the reason and the amount of interest payable.
- Output liability on mismatch:
Any change in sales invoice increases the tax liability and interest is applicable on the increased amount.
- ITC claimed on mismatch invoice:
Any increased change in the tax liability arising due to a change in the purchase invoice and where ITC was also claimed is captured here. Interest is payable on the increased amount.
- Other ITC reversals:
ITC reversals lead to increased tax liability on which interest applies.
- Undue excess claim/excess reduction [Section 50(3)]:
Extra claiming of ITC also leads to interest payable
- Interest credited on correction of mismatch:
Mismatched invoices lead to paying extra interest which is to be credited back to the tax payer
- Interest liability carry forwarded:
Any part payment of the interest leads to a balance interest liability, which is carry forwarded.
- Delayed tax payment:
Any late payment in tax or delayed tax return filing is captured here.
- Total interest liability:
The aggregated interest payable under CGST, SGST and IGST.
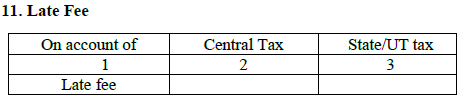
11. Late fees:
A late fees from Rs. 100/- up to a maximum of Rs. 5000/- is also liable to be paid along with interest on delayed return filing. However, there is no late fees on IGST.
Part B [To be manually filled]
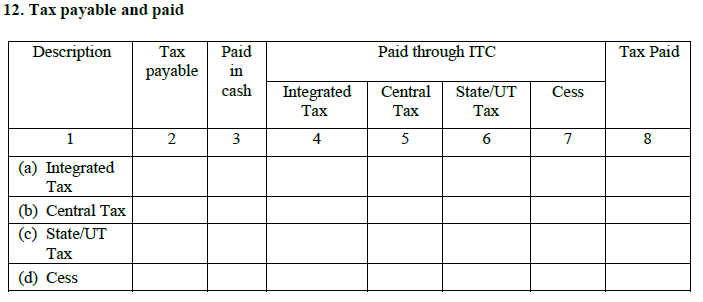
12. Tax payable and paid:
An example would give the much needed clarity. If there is an overall tax liability of Rs. 40000/-, one can pay Rs. 25000/- in cash [column 3] and Rs. 15000/- through using the ITC credit [Columns 4,5 and 6] and complying with the ITC claim provisions.
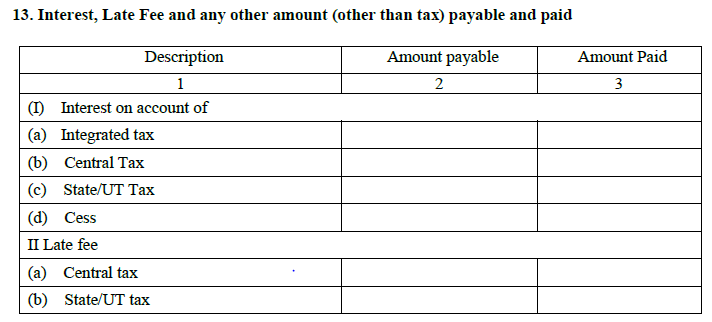
13. Interest/Late fees/any other amount [except tax] payable and paid:
Any amount paid as interest or late fees will come here with the bifurcation of tax heads.
14. Refund claimed from electronic cash ledger:
Any excess payment of tax would be duly returned to the tax payer.
- Refund from cash ledger only applies when all the return related liabilities for the month have been complied with.
- A debit entry will be created in the electronic cash ledger, when the refund claimed is applied via table 14.

Once everything is filled, a declaration is to be electronically signed authenticating that all the given information is proper and accurate.

What if GSTR-3 is not filed / filed late?
If GSTR-3 is not filed, then the GSTR-1 of the next month also could not be filed leading to heavy penalties and fines.
Interest @ 18% per annum and late fees, both are applicable in case GSTR-3 is not filed or filed late.
The interest is computed on the amount of outstanding tax and time period will be considered from the next day of filing [21th of the month] to the date of the payment.
The late fees is Rs. 100/- daily both on CGST and SGST individually making it Rs. 200/- per day up to a maximum of Rs. 5000/- .
Can GSTR-3 be revised?
No, GSTR-3 once filed cannot be revised since the majority of the portion in GSTR-3 auto-populates through GSTR-1 and GSTR-2. Any unintentional error, if somehow made, can only be mended in the next month’s GSTR-1 and GSTR-2 returns.
Due date for GSTR-3:
The latest announcement of the GST council via notification # 29/2017, dated 5th September’17 directs that:
| Month | Due Date for Filing GSTR-3 |
| Jul-17 | Up to 10th of November |
A 5 day gap is gap in given between filing GSTR-2 and GSTR-3 to address any buyer-seller mismatch and discrepancies.
- ★★
- ★★
- ★★
- ★★
- ★★
Check out other Similar Posts
😄Hello. Welcome to Masters India! I'm here to answer any questions you might have about Masters India Products & APIs.
Looking for
GST Software
E-Way Bill Software
E-Invoice Software
BOE TO Excel Conversion
Invoice OCR Software/APIs
GST API
GST Verification API
E-Way Bill API
E-Invoicing API
KSA E-Invoice APIs
Vehicle tracking
Vendor Verification API
Other Requirement